BEARING DATA
Search Boundary Dimensions and Bearing Numbers
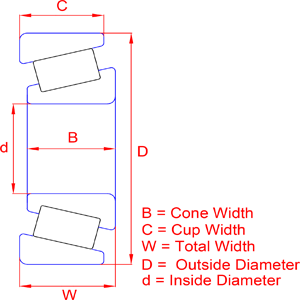
Tapered roller bearings are a type of rolling element bearing designed to support both radial and axial loads. These bearings have tapered inner and outer raceways, with tapered rollers arranged between them. The geometry of the tapered surfaces enables the rollers to guide themselves and distribute loads more evenly. Here's a breakdown of the key components and features of tapered roller bearings: 1. Inner and Outer Raceways: Tapered roller bearings have inner and outer raceways with tapered surfaces. The inner race (cone) and outer race (cup) are designed in such a way that they converge at a common point on the bearing axis. 2. Tapered Rollers: Tapered rollers are placed between the inner and outer raceways. These rollers are conical in shape, and their large end contacts the large end of the cone, while the small end contacts the small end of the cup. 3. Tapered Angle: The angle formed by the tapered surfaces of the inner and outer raceways, as well as the tapered rollers, is critical. This angle is known as the cone angle, and it determines the bearing's ability to handle both radial and axial loads. 4. Axial Load Capacity: Tapered roller bearings are well-suited for applications where axial (thrust) loads need to be supported in addition to radial loads. The tapered geometry ensures that the rollers can accommodate both types of loads. 5. Single Row and Double Row Designs: Tapered roller bearings come in both single row and double row designs. Single row bearings consist of one cone and one cup, while double row bearings have two cones and two cups. 6. Cage or Retainer: To keep the rollers evenly spaced and prevent them from coming into contact with each other, tapered roller bearings often include a cage or retainer. 7. Lubrication: Adequate lubrication is crucial for the proper functioning and longevity of tapered roller bearings. Lubrication helps reduce friction and wear between the rolling elements and raceways. Tapered roller bearings are commonly used in various applications, including automotive, industrial machinery, and heavy equipment, where they provide reliable support for radial and axial loads in both directions. Their design allows for efficient distribution of loads, making them suitable for high-speed and high-load conditions.