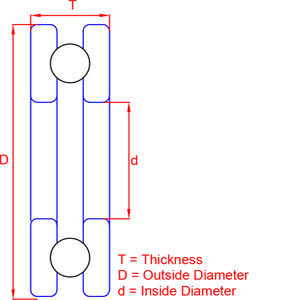
Thrust ball bearings are a type of rotary bearing designed to support axial loads, which are forces parallel to the shaft's axis. These bearings belong to the family of ball bearings, which use balls to reduce friction between moving parts and enable smooth rotation. Unlike radial ball bearings that primarily handle radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft), thrust ball bearings are specifically engineered to handle axial loads. The key features of thrust ball bearings include: 1. Ball Configuration: Thrust ball bearings have a set of balls arranged in a ring-shaped raceway. These balls allow for the transmission of axial loads in a specific direction. 2. Ring Configuration: There are two main ring components in a thrust ball bearing: the shaft washer and the housing washer. These washers are designed to accommodate axial loads in opposite directions. 3. Cage: The balls in thrust ball bearings are usually separated by a cage to maintain equal spacing and prevent them from coming into direct contact with each other. This cage also helps to guide the balls and ensure smooth operation. 4. Single-Direction and Double-Direction: Thrust ball bearings can be single-directional, designed to accommodate axial loads in only one direction, or double-directional, capable of handling axial loads in both directions. 5. Load Capacity: Thrust ball bearings are suitable for applications where axial loads are predominant. They are commonly used in automotive, marine, and industrial applications where there is a need to support thrust loads. In summary, thrust ball bearings are engineered to handle axial loads by utilizing balls arranged in a specific configuration. They play a crucial role in applications where axial forces are present, providing a reliable and efficient means of supporting and facilitating axial movement.
Types of Bearing
Thrust Ball Bearing

© 2024 Engineer Data. All rights reserved. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service
Engineer Data application provides a comprehensive suite of engineering calculations, including:
• Spur Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Helical Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Worm and Worm Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Gear Train Calculation for Helical Gear Cutting on Milling Machine
• Simple Indexing for Milling Machine
• Gear Train Calculation of Differential Indexing for Milling Machine
• Taper Calculation for Lathe Machine Jobs
• Hole Dividing Calculation for Drill Machine
• Bearing Number Identification and search of boundary dimension
Improve your engineering projects with accurate and reliable data. For more information visit Engineer Data
Engineer Data application provides a comprehensive suite of engineering calculations, including:
• Spur Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Helical Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Worm and Worm Gear Cutting Calculation on Milling Machine
• Gear Train Calculation for Helical Gear Cutting on Milling Machine
• Simple Indexing for Milling Machine
• Gear Train Calculation of Differential Indexing for Milling Machine
• Taper Calculation for Lathe Machine Jobs
• Hole Dividing Calculation for Drill Machine
• Bearing Number Identification and search of boundary dimension
Improve your engineering projects with accurate and reliable data. For more information visit Engineer Data









